Selank Overview
Selank, which was developed in Russia, is a short peptide with nootropic and anxiolytic properties. It is a synthetic analogue of naturally occurring Tuftsin, an immunomodulatory peptide that modulates IL-6, T helper cells, monoamine neurotransmitters, and brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF). In fact, Selank and Tuftsin are essentially the same except that Selank has an additional four amino acids in its chain that help to improve metabolic stability and half-life.
Selank has been tested in clinical trials as a potential treatment for generalized anxiety disorder.
Selank Structure
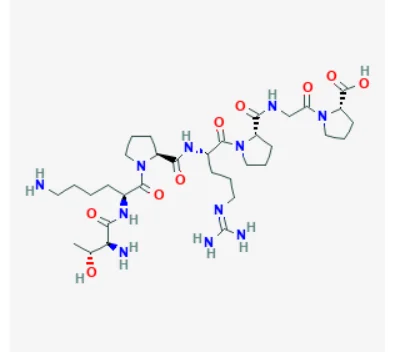
Sequence: Thr-Lys-Pro-Arg-Pro-Gly-Pro
Molecular Formula: C33H57N11O9
Molecular Weight: 751.887 g/mol
PubChem CID: 11765600
CAS Number: 129954-34-3
Synonyms: Selanc
Selank Research
Selank Anxiety Effects Based on Genes Related to GABA Neurotransmitter
According to Dr. Anastasiya Volkova of the Institute of Molecular Genetics in Russia, “numerous clinical studies have shown that Selank has strong antianxiety and neuroprotective effects in the treatment of anxiety. The clinical effects of Selank are similar to those of the classical antianxiety medications such as benzodiazepine, which are allosteric modulators of GABAA receptors and increase the inhibitory action of GABA.” Selank’s effects include reducing anxiety, improving mood, lower stress levels, and positively influencing memory and learning. Like benzodiazepines, low doses of Selank have a sedating effect. Unlike benzodiazepines, Selank does not appear to be habit-forming and does not lead to symptoms of withdrawal or amnesia.
Research in rats shows that of the 84 genes known to be connected to GABA signaling in some way, seven are heavily modulated by Selank and 45 show some change in expression when the peptide is administered. Overall, 52 genes related to GABA signaling are affected by Selank to some degree. These results indicate that Selank can directly influence the expression of genes in nerve cells and that it likely produces effects by changing the affinity of the GABA receptor for GABA[1]. This alteration of receptor affinity likely explains why Selank is synergistic with benzodiazepines and other GABA receptor agonists.
Research in rats shows that Selank and benzodiazepines, when used alone, have similar effects on anxiety, particularly generalized anxiety disorder. Selank may hold a slight advantage over benzodiazepines when attempting to reduce elevated levels of anxiety, but a combination of the two treatments appears to be the best in treating unpredictable chronic mild stress[2].
The effects that Selank has on GABA receptors may be modulated, to some degree, by the peptide’s effect on enkephalin degradation. Testing indicates that people with anxiety and phobic disorders demonstrate increased enkephalinase activity in the blood during generalized anxiety and, as a result, the enkephalins they produce have shorter half-lives[3]. By preventing degradation of enkephalins through enkephalinase inhibition, Selank may be resetting this enzymatic pathway and helping to protect the body’s natural anxiolytic peptides. Research in mice prone to anxiety supports the hypothesis that at least part of the impact that Selank has is a result of preventing enkephalin degradation[4].
Selank and the Immune System in Anxiety
Research in patients with depression indicates that Selank can suppress the gene responsible for the production of the inflammatory cytokine IL-6. Interestingly, this effect is only seen in patients with depression and does not appear to take place in healthy individuals[5]. This suggests that Selank may be useful in treating people with anxiety-asthenic disorders, severe disorders in which anxiety is associated with fatigue, headache, heart palpitations, high blood pressure, nerve pain, and depression.
When comparing Selank to standard anxiolytic treatments, like benzodiazepines, the two treatments show similar benefits in reducing anxiety, but only Selank has any effect on asthenic symptoms like fatigue and pain[6]. Part of the effect is likely due to Selank’s ability to modulated IL-6 expression while part is likely due to the peptide’s ability to alter the rate of breakdown of the body’s natural pain killers, enkephalins.
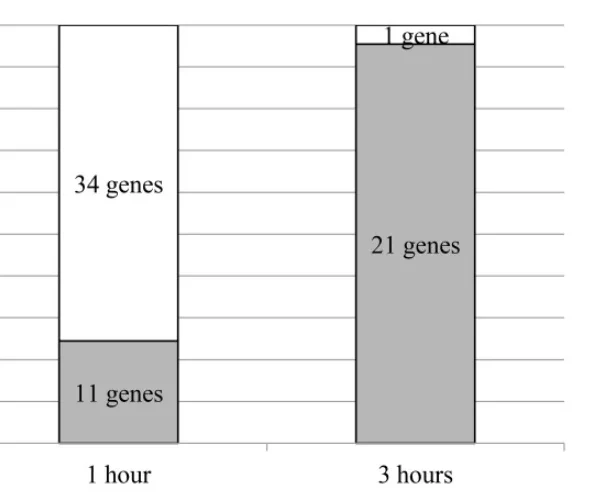
Testing of Selank in rats has revealed that the peptide regulates the expression of some 34 genes involved in the inflammatory process. These genes affect chemokines, cytokines, and receptors for both. In particular, Selank has been found to alter expression of BcI6, a gene that is heavily involved in the development of the immune system[7]. This study, more than any other, revealed that Selank has very complex biological effects, but may help to deepen our understanding of how the immune system develops.
Selank and even fragments of Selank have been shown to temporarily alter gene expression for C3, CAsp1, Il2rf, and Xcr1 in the mouse spleen. By affecting these genes, Selank is able to alter the balance of the immune system and thereby modulate inflammation[8].
Selank Research with Memory and Learning
There has long been an association between anxiety and learning/memory. The correlation is a negative one, with increased anxiety leading to decreased ability to recall memories or store new information. Traditional anxiety treatments can reduce this effect, as can Selank, but Selank appears to do more than simply reduce the impact of anxiety on cognitive function. There is good reason to believe that Selank actually boosts cognition directly.
Research in rats trains with food rewards and injected with either saline or Selank has shown that Selank boosts memory trace stability and thus enhances the memory storage process[9]. It is important to note that this benefit was seen regardless of the anxiety levels of the rats, indicating that the peptide has effects beyond its ability to simply reduce stress-related impairment of memory.
It appears that Selank may alter memory by affecting the expression of a number of genes in the hippocampus. Research in rats shows changes in mRNA levels of 36 different genes after intranasal administration of Selank. Most of the genes encode proteins associated with the plasma membrane and may therefore modulate ion-dependent processes in learning and memory[10]. Though much research needs to be done to understand the mechanism by which Selank works to improve memory and learning, this research offers a tantalizing early clue to suggest that it alters the way neurons function in such a way that both forming and accessing memories is easier.
Research even suggests that Selank can help to rescue memory and learning following damage to the brain. Rats treated with a neurotoxin and then Selank showed restored cognitive processes in at least one study. This effect appears to be related to an artificial inhibition of the catecholamine system in the brain by Selank[11]. There is some hope that Selank will help to shed light on how cognitive function can be restored or at least improved following traumatic brain injury, particularly the kinds of injury that occurring during the birth process.
Selank Research and Pain
Selank may act to reduce the degradation of natural enkephalins by inhibiting the enzymes, found in human blood, that break them down[12]. Enkephalins are natural peptides that bind to opioid receptors and help to blunt the severity of pain. They also function in the human stress response and are found in high levels in the brain and adrenal glands. By reducing levels of enkephalins in the brain, Selank may help to blunt the normal stress response and the effects that it has on memory, learning, and concentration.
Selank exhibits minimal side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. Selank for sale at Peptide Sciences is limited to educational and scientific research only, not for human consumption. Only buy Selank if you are a licensed researcher.
Epithalon Research
1. The Role of Telomerase in the Anti-Aging Effects of Epithalon
Early research using insects and rodents revealed that epithalon can prolong life substantially. In normal, healthy fruit flies and rats, epithalon decreases mortality by 52%. In mice prone to both heart disease and cancer, epithalon prolongs life by as much as 27% compared to controls[1]. At least part of the answer to how epithalon achieves these profound effects is via its elimination of free radicals (charged molecules that do damage to healthy tissue).
Anti-oxidant activity is not the only reason that epithalon extends life, however. There is good evidence from in vitro experiments on human somatic cells to show that epithalon activates an enzyme called telomerase[2]. Telomerase protects telomeres, the ends of chromosomes that are critical to ensuring the health of DNA. Epithalon’s activation of telomerase leads directly to a decrease in how many errors a strand of DNA contains, supporting the notion that epithalon protects DNA from damage[3], [4]. In short, epithalon protects DNA from accumulating errors over time, a process that eventually leads to cell dysfunction, aging, and even cancer in some cases.
2. Epithalon and DNA Activation
Neither its impact on free radicals nor its effects on telomeres seem sufficient to explain the profound effects that epithalon has on longevity. Indeed, scientists are working hard to understand how this short peptide achieves the effects that it does so that the mechanisms can be explored in depth. As it turns out, at least part of the answer may come from the fact that epithalon changes the expression of certain genes.
Research in cell cultures shows that epithalon interacts directly with DNA to turn on and enhance the expression of certain genes. Epithalon interacts with the promoter regions of genes for CD5, IL-2, MMP2, and Tram1[5]. CD5 and IL-2 both affect the function of the immune system while MMP2 plays a critical role in the maintenance of extracellular matrix in skin, tendons, and other connective tissue. These findings suggest that epithalon may impact the function of the immune system and the ability of the body to heal itself following not only injury, but following typical day-to-day stress as well.
It is not surprising that epithalon impacts the immune system. Research in rats indicates that epithalon boost the expression of interferon gamma in aging lymphocytes[6]. Interferon gamma is a critical signaling molecule in the immune system. It is important for fighting off viral infections through the activation of macrophages, natural killer cells, and T cells.
The following are known DNA interactions of epithalon:
- CD5 – Leads to immune cell differentiation
- IL-2 – Increases IL-2 production, which regulates white blood cells
- MMP2 – Enhances MMP activation and decreases inflammation
- Tram1 – Enhances protein production
- Arylalkylamine-N-acetyltransferase – Enhances melatonin production
- pCREB t – Circadian rhythm regulation and anti-neoplastic effects
- Telomerase – Telomerase activity increases cell longevity
3. Epithalon and Skin Health
As stated above, epithalon has a positive effect on the gene that regulates MMP2. MMP2 is a protein found in connective tissue like skin. Research in rodents indicates that not only does epithalon activate this gene, it activates fibroblasts, the cells that produce and maintain MMP2 as well as other components of the extracellular matrix like collagen and elastin. Mice exposed to epithalon show an increase in fibroblast activation of 30-45%[7]. By activating fibroblasts, epithalon can help to boost rates of healing and offset the natural decline in skin structure and integrity that occurs with aging.
Further evidence for epithalon’s benefit in skin comes from the fact that it decreases caspase-3 activity. Caspase-3 is an enzyme in the apoptosis or programmed cell death pathway. By decreasing caspase-3 activity, epithalon helps to protect fibroblasts and other skin cells, keeping them alive and healthy for longer periods of time[8].
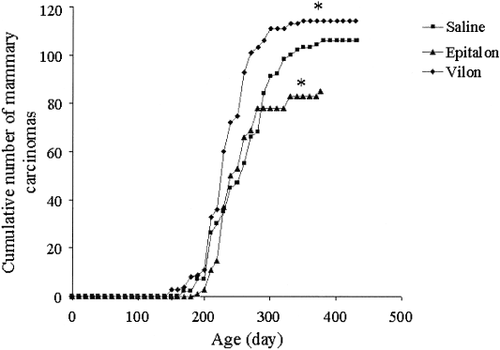
4. Epithalon and Tumor Growth
Daily administration of epithalon to rats with cancer has been found to decrease tumor growth[9]. Not only does the peptide reduce tumor growth, it prevents the metastasis or spread of these tumors to distant tissues as well[10], [11]. Epithalon is currently being investigated as a potential treatment for Her-2/neu positive breast cancers and is of interest in preventing the development of certain types of leukemia as well as testicular cancer[12], [13].
There is some evidence that epithalon activates the gene for PER1 protein, which is found in the hypothalamus. PER1, which helps to regulate circadian rhythm, is under-expressed in cancer patients. It is unclear if this under-expression precedes cancer development and therefore contributes to cancer growth or is a consequence of cancer development. It is clear that the protein affects cancer growth once the cancer is established. Control of PER1 expression may be one means of naturally slowing tumor growth. Research shows that PER1 expression sensitizes cells to the effects of radiation and may therefore help to decrease the doses of radiation needed to treat certain cancers, a fact that would not only offset immediate side effects, but reduce the occurrence of secondary tumors following high doses of radiation[14].
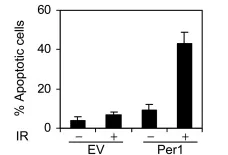
PER1 Causes Increased Rates of Ionizing Radiation-Induced Cell Death
Source: Molecular Cell
5. Epithalon and Melatonin Secretion
Melatonin, which is linked to sleep and aging, is produced by the pineal gland. Research in rats shows that epithalon and similar peptides affect both the synthesis and release of melatonin by affecting the expression of two proteins (arylalkylamine-N-acetyltransferase (AANAT) and pCREB transcription protein)[15].Both of these genes play an important role in melatonin production and in the circadian (day/night) control of melatonin release. Research in monkeys indicates that epithalon restores melatonin secretion to normal[16].
6. Epithalon and Eyesight
A trial in rats suffering from retinitis pigmentosa found that epithalon improves outcomes in 90% of patients[17]. It appears that the peptide helps to preserver normal structure of the eye while boosting the bioelectric function of the retina necessary for vision.
Epithalon exhibits minimal side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. Epithalon for sale at Peptide Sciences is limited to educational and scientific research only, not for human consumption. Only buy Epithalon if you are a licensed researcher.